Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery
At CHOC, our board-certified neurosurgeons bring the highest levels of expertise and experience to even the most complex disorders of the brain, spine and central and peripheral nervous systems. Our techniques used in minimally invasive surgery improves accuracy and significantly reduces surgery/anesthesia time, so childhood doesn’t have to be put on pause.
What is minimally invasive surgery?
Minimally invasive surgery refers to any surgical procedure that is less invasive to the body, as opposed to the traditional open surgery method. Small tools, cameras and lights are used to view the body and perform the procedures via tiny incisions. This method limits openings of skin and muscle for surgery.
What are the benefits of minimally invasive surgery?
Since minimally invasive surgery utilizes special tools to see and perform procedures inside the body, smaller incisions are made compared to open surgery. These smaller incisions lead to many benefits, including:
- Less pain: With the absence of open surgery, the patient’s body is receiving less trauma, resulting in less pain and discomfort.
- Quicker recovery time: The incisions from minimally invasive surgery heal a lot faster than open surgery due to their size. Patients can resume their daily activities in a significantly shorter time.
- Shorter hospital stays: Patient’s hospital stays depend on the surgery, but most patients can go home after one to two nights in the hospital.
- Minimal scarring: Smaller incisions equal less scarring. Stitches often cause scarring, and with minimally invasive surgery the incisions are smaller, resulting in less stitches.
- Lower rate of complications: In minimally invasive procedures, advanced tools and in some circumstances, robotics are used to operate. These instruments help to have more precise control during surgery and increase the accuracy. Blood loss is a serious complication during surgery but using minimally invasive techniques this complication is minimized.
While there are many benefits to a minimally invasive surgery, this method might not work for every condition. At CHOC, we strive to make this a possibility for every patient. Make sure to consult with your doctor if minimally invasive surgery is right for your child.
Minimally Invasive Neurosurgery Equipment
There are multiple tools that allow surgeons to perform minimally invasive neurosurgery. A main tool used in brain surgery is an endoscope. An endoscope is a long tube with a camera and light attached.
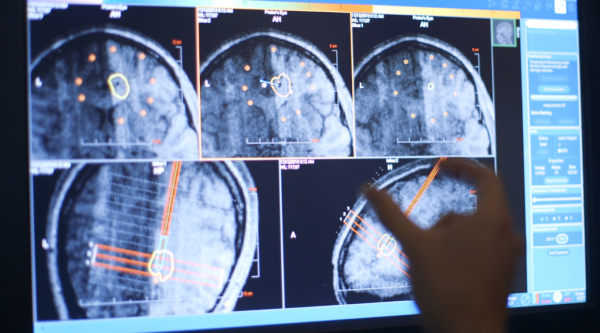
Some minimally invasive neurosurgeries use robotic assistance equipment. At CHOC, we use a surgical robot called a ROSA (Robotic Stereotactic Assistance). Through image guidance and a robotic arm (that’s under the neurosurgeon’s control), it is able to perform procedures with more precision, accuracy, and safety. A ROSA is sometimes utilized for laser probe and electrode placement in the brain. During brain surgery, the ROSA acts as a GPS, providing an extensive map that allows us to target specific areas deep in the brain. It can be used for many neurosurgeries including but not limited to, deep brain stimulation, laser ablation and responsive neurostimulation.
Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a surgical treatment for uncontrolled and abnormal movements. There are two different procedures for DBS, two-stage and three-stage. The procedure chosen depends on your child’s condition.
Deep brain simulation can be used for conditions like:
- Primary dystonia
- Secondary dystonia
- Epilepsy
- Cerebral palsy
- Chorea
- Tremors
- Tourette syndrome
Using the ROSA’s mapping robotic system, neurosurgeons can locate the exact area to operate and use the ROSA to implement the electrodes into target areas. Electrodes are thin wires that produce electrical impulses. In both two-stage and three-stage surgery, two minimally invasive holes are made in the skull for electrodes to be placed in the brain. Then, the electrodes are connected via wires to a stimulator device in the chest. The device acts as a pacemaker by sending impulses to the electrodes that signal the brain to stop or minimize uncontrolled movements.
Using the ROSA allows surgeons to be more precise, resulting in a safer and better outcome for your child.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Vagus nerve stimulation utilizes a small pacemaker like device to send electrical impulses to the brain via the vagus nerve when seizure activity is detected. This treatment is utilized for children with seizures that cannot be controlled through medication. The vagus nerve runs from the brain stem, through the neck to the abdomen.
A small incision is made on the outside of the chest to implant the VNS device. In order to connect the device to the vagus nerve, a second small incision is made on the lower neck along a crease of skin. From this incision, the wires of the device are threaded under the skin and wrapped around the left vagus nerve. The stimulator is pre-programmed, by your child’s doctor, to send electrical impulses to the vagus nerve via set cycles. The duration, frequency and current of the stimulation is dependent on your child’s condition, symptoms and side effects. If a child feels that a seizure is about to happen, the VNS can also be activated manually by holding a special magnet near their implant. In some instances, this can stop a seizure when used shortly after onset.
Responsive Neurostimulation
Responsive neurostimulation (RNS) is a surgery to help treat seizures. The RNS System is a small neurostimulator that is implanted during surgery. The device is placed within the skull and is connected to two wires that are placed on the surface of the brain, in the brain, or a mixture of both. This surgery is minimally invasive and does not require any tissue removal.
Once implemented, the neurostimulator monitors and responds to brain waves to detect seizure activity. When this activity is detected, the stimulator sends a signal of electrical current to the brain to stop the seizure or possibly prevent the seizure. The RNS System wirelessly collects information from the neurostimulator and uploaded to a database where your doctor can review your child’s seizure activity and progress.
With responsive neurostimulation being a minimally invasive surgery, most patients can go home the next day.
Endoscopic Neurosurgery
Endoscopic neurosurgery is a minimally invasive surgery used to identify and treat conditions deep in the brain. An endoscope is inserted into the brain through a small incision in the skull. In some cases, the tube is inserted through the nose and can avoid incisions altogether. Images from the endoscope are magnified in the operating room and allow for a deeper, more extensive view of the brain, leading to increased procedure accuracy. This method can be used for a variety of brain conditions, including:
Endoscopic neurosurgeries can replace larger, more invasive methods and achieve great outcomes. The lack of large incisions results in faster and safer procedures.
Laser Ablation
Laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT) or laser ablation is the latest advancement in minimally invasive neurosurgery. Laser ablation is used to destroy any abnormal tissue and/or tumors in the brain. First, a small hole is made where a laser probe is placed in the skull. Using MRI visualization, the ROSA plans the entry point and trajectory to increase the laser precision. Once the area is determined, heat is delivered to the targeted area using a laser controlled by the neurosurgeon. The ROSA allows the surgeon to effectively locate the target point and avoid hitting blood vessels and surrounding tissue.
Laser ablation is useful for patients with epilepsy or tumors, especially when they are deep in the brain. ROSA is able to increase surgical accuracy when removing the tumors, lesions and/or tissue where seizures occur, making it a safer surgery for patients. With laser ablation being a minimally invasive surgery, most patients are able to go home the next day.
CHOC Neuroscience Institute

We know that managing your child’s neurological condition can be scary. At CHOC, our neuroscience-trained team will be with your family from diagnosis throughout your child’s growth to ensure the best possible outcome.
The CHOC Neuroscience Institute is at the forefront of utilizing this advanced technology to provide the best pediatric neurosurgery treatment for children in a minimally invasive way.












